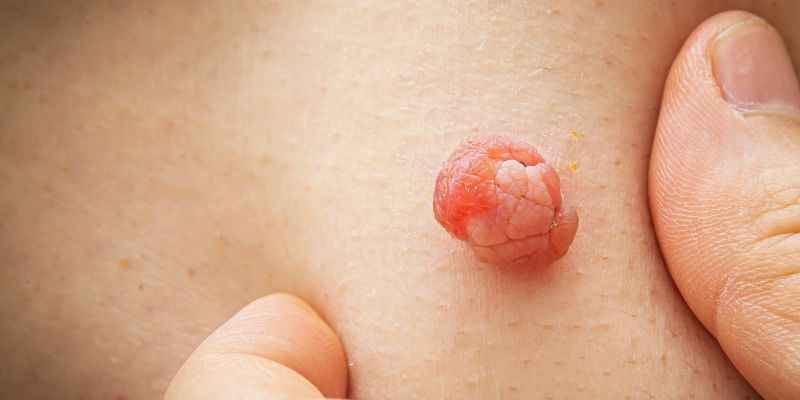
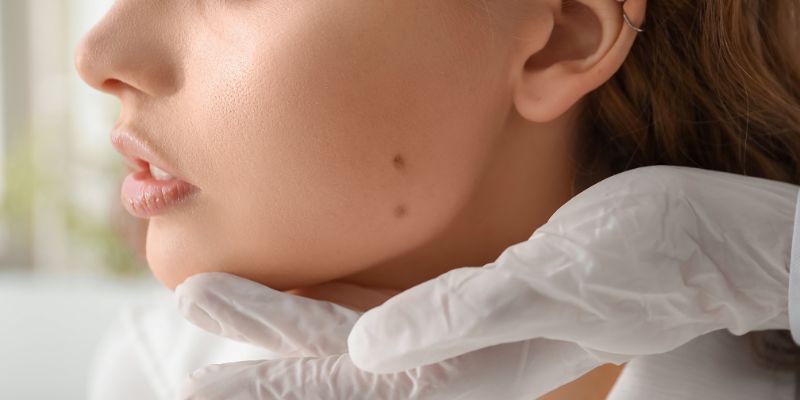
A mole is a typical form of skin growth. It is also known as a beauty sign or nevus. Moles can develop anywhere on your skin, including the scalp, eyes, nails, hands, and feet, singly or in clusters. In childhood and adolescence, the majority of people develop 10 to 45 moles. They are frequently seen as tiny, dark brown dots that are brought on by concentrations of melanocytes, which are cells that create pigment.
Moles typically get lighter in color and higher as the years go by. Hairs sometimes grow on the mole. Over time, some moles will gradually vanish, while others won't alter at all. The majority of moles are not harmful. They rarely develop into cancer. So, keeping an eye on moles is crucial. If you want to know more about them, continue reading, as this article is a complete guide about moles!
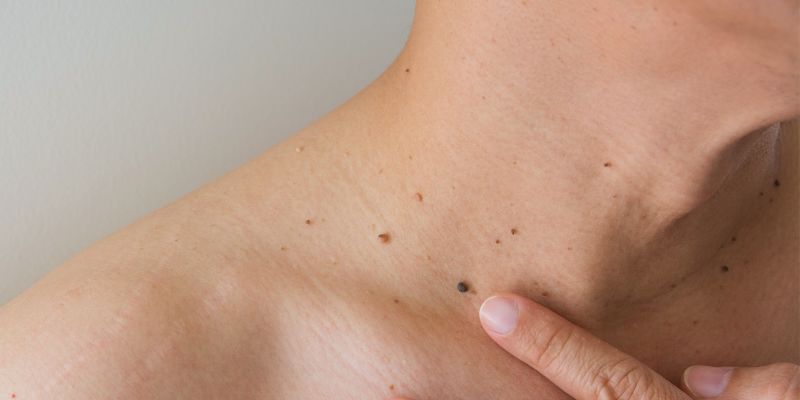
What are the Types of Moles?
Moles are of different types; lets know about them all here one by one:
Congenital Moles
Congenital moles are the initial kind of moles. It indicates that you had the mole by birth. Since one in every 100 persons is born with a mole, this is a rather typical condition. Congenital moles may differ in size from little to huge. They come in a variety of colors and can be plain. Compared to moles that develop after birth, these moles may have a higher chance of turning into melanoma. Your skin mole has a higher chance of developing into cancer if it is more than eight millimeters in diameter.
Acquired Moles
Acquired moles appear in childhood and later in life. They were brown and were caused by sunburn. Mostly they were circular, and stay the same as you get older. These moles are not always transformed into melanoma. They typically appear as a scattered pattern with darker patches on the cheeks, ears, and limbs of people with olive or dark complexion. It is normal and does not indicate that the mole is cancerous. However, you might be more susceptible to melanoma if you have 50 or more of these moles.
Atypical Moles
The risk of atypical moles developing into cancer is higher than that of congenital and acquired moles. Atypical moles have unevenly formed boundaries and are slightly bigger than acquired moles. They frequently have an array of shades, such as pink, white, brown, black, and tan. They also increase the possibility of developing melanoma, which can be bright, darker, or maybe glossy black. Dysplastic nevi and Clark's nevi are examples of atypical moles.
Spitz Moles
These unevenly sized moles are bigger than a pencil eraser. The mole may appear to be red, black, or brown. Those that have these moles may have more than 100 of them, and they are typically inherited. You need to be conscious that this kind of mole can leak fluid or bleed. Skin cancer is not caused by having moles. You are more likely to acquire malignant (cancerous) melanoma if you have dysplastic moles. So, it's time to consult with a dermatologist and examine whether the mole is cancerous or not.
Dermal Moles
A large mole that is typically sensitive to feel might be either dermal or intradermal. The color of dermal moles may match or be brighter than the nearby skin. Its outer layer could be smooth or uneven. It appears near the nose. Because they can become uncomfortable or inflamed by clothing, combs, or razors, dermal moles are often frustrating. With radiofrequency surgery or shave removal, this kind of mole can be easily removed with minimal scarring.
What are the Common Causes of Moles?
There are many factors responsible for moles; a few of them have been mentioned below:
- Sun Exposure: Moles can develop from ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun. They are more prone to appear on skin that is regularly exposed to UV radiation.
- Genetics: Many individuals have a genetic susceptibility to moles. Moles are prone to appear in family members of those who get them immediately.
- Fairer Skin: Moles are more common in those with less pigmented skin.
- Immune System: Those with poor immune systems and who suffer from various diseases are more likely to face this problem.
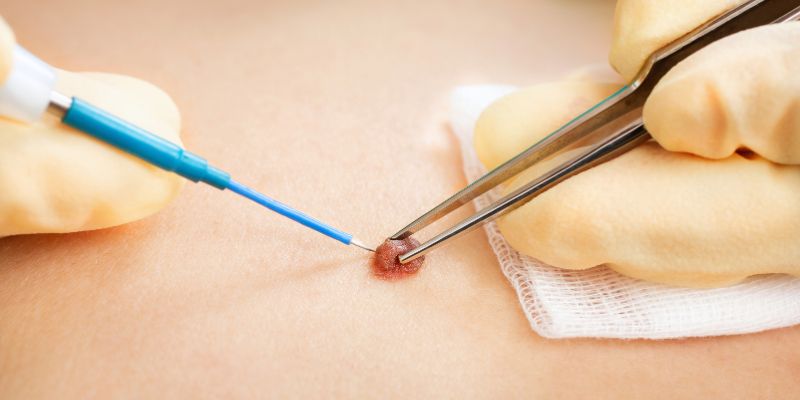
How Are Moles Removed?
The majority of skin patches that resemble moles don't require removal. If a mole appears to be dangerous or is bigger than usual, your doctor can advise having it removed. The doctor will provide anesthesia to numb the region if you want to have a mole removed. After that, they will either use a surgical blade to cut or shave the mole off or punch equipment, which is an empty tube with a sharp edge.
You might need stitches in the affected area to cover the cut and keep it hygienic until your skin repairs. Following a mole removal, you should sterilize the area around the wound and, if necessary, take painkillers. Inform your physician if the wound becomes red or swollen or if the pain or bleeding gets worse.
Right Ways to Remove Moles At Home
Moles can be removed at home using various strategies. Anyone using these treatments should pay close attention to the instructions and be mindful of the risk of skin injury, inflammation, and scarring. They include:
- Garlic: Acids found in garlic may break down the mole-causing cells. But it may cause skin burns.
- Lemon Juice: The mole may become smaller if you use lemon juice more than once a day.
- Honey: Honey possesses antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant qualities. Some people think that if you put honey in moles, they will go away within a few days.
- Castor Oil and Baking Soda: Castor oil and baking soda are combined to make a gel that, if used frequently for a few weeks, gets rid of moles.
Can Moles Be Prevented?
Moles are usual skin development that cannot be avoided. But you can take preventative measures to avoid skin cancer or detect it early by:
- Reducing the amount of sunlight you receive
- Putting on sunscreen each day
- Checking your moles every month to inspect abnormalities
Monitoring your moles improves the probability of finding and curing melanoma and other skin cancers.
Conclusion:
Moles are a common problem. Some people have moles by birth, but they are more likely to appear in later childhood and adulthood. The majority of moles do not develop into cancer, but if they do, they can be fatal if not detected in time. Self-checks and being aware of your skin might be beneficial. You can consult a dermatologist for mole removal, or you can try some home remedies to prevent this problem.